
Prof. Daniel Kamenetzky
Sports Performance Specialist
CONTENTS
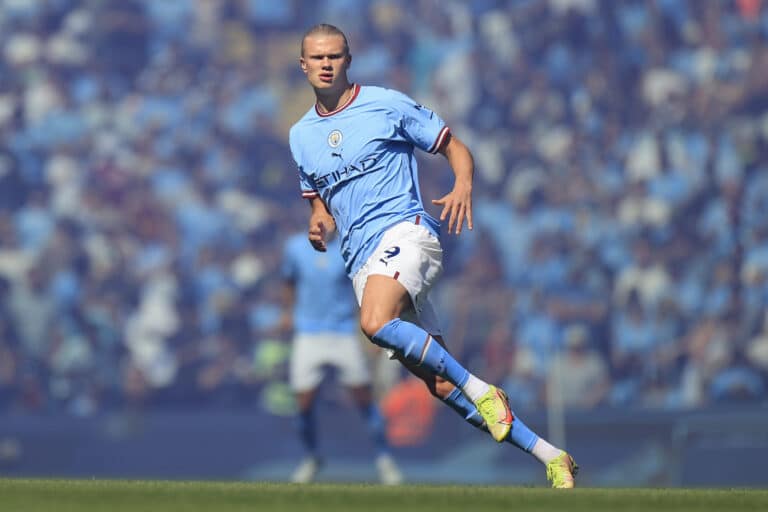
Erling Haaland was ruled out of Manchester City’s visit to Newcastle United in the Premier League, due to a reported foot injury, and is expected to remain out of action throughout the rest of the month. What are the contributing factors that led to the injury and the risk factors in Haaland’s style of play for future injury?


Sports performance expert Professor Daniel Kamenetzky is the founder of Spandrel Analytics, providing data-driven sports performance consulting services in professional sport. In this article, Daniel pulls together a wealth of scientific sports injury knowledge, performance data and observations, to provide injury analysis of Erling Haaland.
A pattern observed 2 years ago...
In February 2022, Spandrel Analytics published an analysis of Haaland’s performance, where we highlighted numerous aspects linked to his recurrent injuries. We also elucidated how these technical limitations had a significant probability of leading to additional and new damage.
Playlist
Haaland's foot injury?
“ Hopefully at the end of this month he'll be ready. It was a little bit more than we expected in the beginning.
“ It's the bone. It needs time. With every injury you can do whatever you want but it's a question of time. ”Pep Guardiola (Jan 12, 2024)
Haaland has been sidelined since mid December 2023 with what Guardiola has described as a ‘bone stress reaction.’
As there is no detailed public diagnosis available, I suggest revisiting the most commonly used techniques in soccer and analyzing how he is executing them.
This could help infer the most probable injuries and their potential locations at this point.
External foot border?
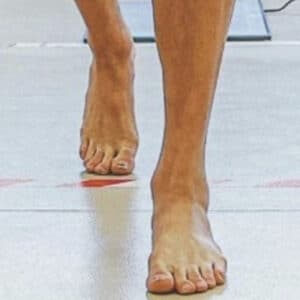
Upon analysing the running and kicking technique, an observable trend is an overload on the external aspect of both feet. This external loading appears to be unsuitable for the foot’s structure, especially when considering Haaland’s body weight and speed.






Running foot load?
The load on the foot is determined by the interplay of factors such as the contact area, time spent on the ground, step frequency, body weight, and the height of the running parabola.
In Haaland’s case, all these elements appear to be inefficient, resulting in a clear overload on the external bones that are not anatomically prepared for such stress.
One prevalent injury in runners with poor technique is the fracture of external foot bones, most commonly the fifth metatarsal, a scenario consistent with Haaland’s technical situation.
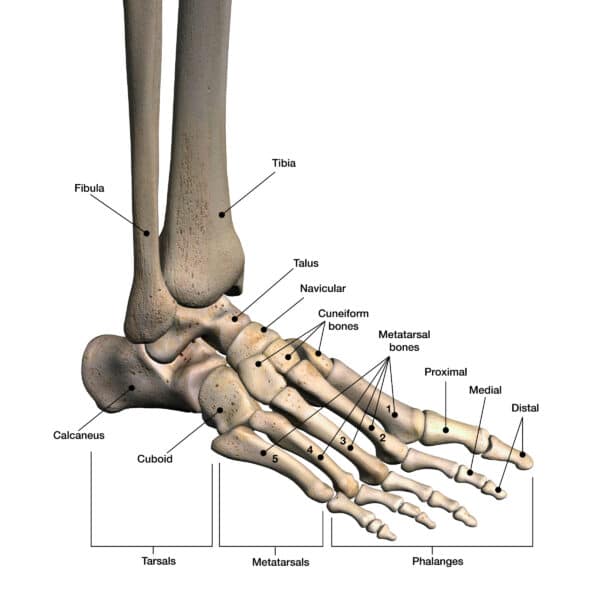

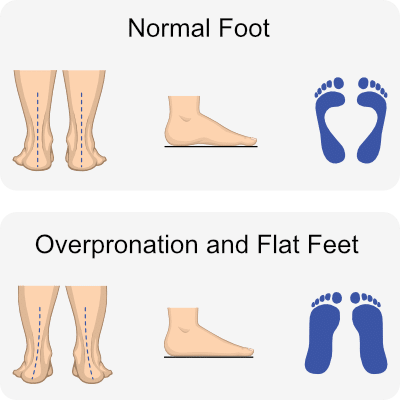
Foot arch overload and flattening?
We also observe that the foot tends to land in an outward position. This tendency places an excessive load on the internal aspect of the knee, external aspect of the ankle, and arch of the foot.
The angulation of the foot in relation to the direction of movement aligns with characteristics seen in conditions like plantar fasciitis or pain in the arch.
In Haaland’s case, this situation is further exacerbated by his body weight, intensifying the stress and flattening of the foot in the mid stance position.
Over time, micro tears in the arch tissue may develop, leading to severe pain that restricts the loading of the area.
Therefore, we can also consider this as another potential source of injury.



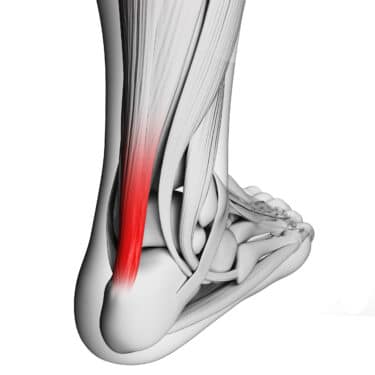
Heel/achilles tendon overload?
When analysing his running technique from the sagittal plane (the vertical anatomical plane that divides the body into left and right), it is evident that his landing consistently occurs in front of the centre of gravity.
This results in ground contact ahead of the hip, generating stopping forces that overload various structures in the leg and lower back, beginning with the heel.




Another vulnerable area that may be affected is where the Achilles tendon inserts, constantly subjected to impact against the ground and/or tensile stress, posing a high risk of inflammation and potential damage.

Right foot inversion and left leg external rotation?
During kicking, there is a rolling out and inversion of the right supporting foot, accompanied by an external rotation of the left kicking leg.
Consequently, the left foot bears the impact from the ball and potential internal foot muscular tensions. The load on the knee might be more significant than on the foot.




As for the right foot, the load at the ankle and knee levels could be more damaging, compounding the stressors mentioned earlier.
A consequence of previous injuries?
It is also possible that he sustained damage during one of the many ankle injuries he experienced in his recent games. However, a player of his stature would typically require a significant impact and/or an already weakened structure for damage to occur.
Therefore, a plausible hypothesis is linked to a pre-existing weakened structure that becomes injured as a result of a severe contact encounter with another player or environmental elements, such as the ground or the goal post.


High stopping forces on the left foot
A recent event resulted in an injury that kept Haaland off the field.
Injuries in the same anatomical area tend to be related
We can observe that the descriptions provided in this report are also consistent with previous injuries. Typically, injuries are interconnected rather than isolated events. As suggested two years ago in our previous report, if techniques are not enhanced to meet the required demands of the sport, the risk of injuries will persist, now heightened by the recurrence and accumulation of damage.

Additional evidence of load distribution on the foot
The placement of a damaged boot may indicate an area of overload and the direction of applied forces.Toes not aligned with the foot axis
It indicates an applied load at an angle to the foot axis.



Damage to the foot
Blisters, black toes (hematomas), and calluses, when consistently present, are possible indicators of overload in those areas.


Conclusions
Two years ago, we identified potential injury risks that are now becoming apparent. The primary source of these injuries appears to be linked to his technical capacity.
Clear evidence has emerged regarding the connection between his running technique and anatomical changes, including toe misalignment, foot damage, and recurrent associated injuries.
However, we currently lack information about the training strategy, which is crucial for identifying other potential contributors to the current injuries, such as the distribution of load and physiological capacity.

